At Colonial Metals Group, our mission is to inform our clients about economic changes that may affect retirement accounts.
How do inflation and market sentiment influence gold’s price per ounce?
Gold’s value tends to rise in tandem with investor demand. This is called price elasticity. And the greater the demand, the greater the elasticity and the higher the price tends to rise. What sets gold apart from traditional assets is its ability to perform well under both favorable and unfavorable economic landscapes. Historically, gold has gained value when the economy struggled and retained its value when the economy thrived
During times of economic uncertainty, many investors turn to gold to hedge against loss and enjoy potential gains. When the Great Recession struck, for example, investors rushed to gold when the stock market fell, and gold was trading at $700 per ounce. Gold’s price then surged and climbed for more than 2.5 years – even as the economy began to recover. By 2011, the price of gold had reached $1,825.
How are gold prices affected by supply and demand?
Gold is a financial instrument and a worldwide commodity. However, gold is not a consumable resource like soybeans, coffee or oil. Nearly all the gold ever extracted still exists in some form, and more gold is being mined each day. It may seem gold prices would decline due to the steady supply. But historical data shows gold has only risen in price over the long term.
Why? Because worldwide demand for gold is growing, and the supply – although continuous – is not keeping up. And when demand outpaces supply, gold prices tend to rise.
Additionally, most investors hold their gold for years which removes that gold from the market. Gold held as jewelry is also kept for many years or passed down as an heirloom. As a result, the relatively small amounts of gold mined each year cannot meet growing demand, and this exerts further upward pressure on gold’s price.
How do central bank gold purchases affect the price of gold?
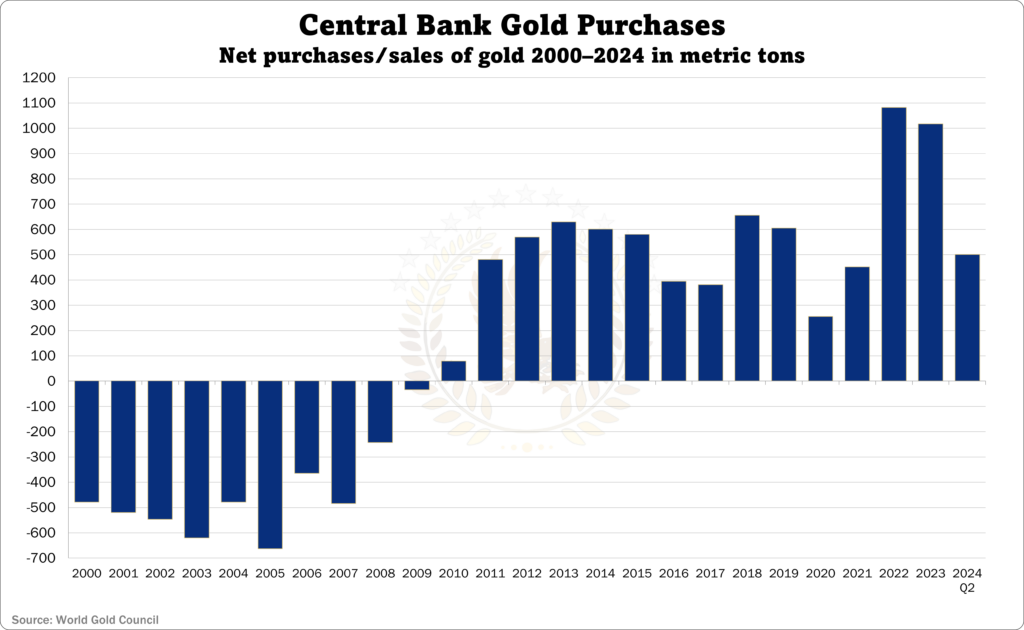
Central banks consider gold money, and they hold large reserves as a currency that can’t be printed and isn’t dependent on any other country,
Ultimately, central banks are businesses that expect to generate a profit from their investments. So, when the economy is strong and central banks have plenty of foreign exchange reserves, they sometimes sell a portion of their gold holdings to invest in other assets that might deliver higher returns.
However, the timing of those sales is challenging. Because they know selling large quantities when market demand for gold is low may negatively impact its price and diminish their potential returns. To avoid this,13 major central banks signed The Washington Agreement on September 26, 1999, which limited their collective gold sales to 400 tons per year.
This agreement helped stabilize the gold market for years and was renewed in 2004 and 2009. However, in 2010, central banks started buying large quantities of gold, and the agreement was not renewed.
So, yes – central bank gold sales can impact gold prices, especially when the economy is good, and gold demand is soft. But major central banks try to coordinate their sales to avoid flooding the market. And over the last few years, they’ve become net buyers of gold.
As a result, we’ve seen gold’s price rise dramatically.
What is today’s spot price for an ounce of gold?
Like any other commodity, the spot price of gold per ounce fluctuates constantly during standard trading hours. To help you stay informed about the current gold price and historical trends, Colonial Metals Group provides live gold prices and historical data on our website. You can find the most up-to-date gold spot price displayed prominently at the top of every page on our site, so you always have access to real-time information.

Claim You Free
2024 Gold Guide








